Keywords in java are static mainly used for memory management. We can apply java static keywords in variables, methods, blocks and nested classes. static Keywords belong to classes, not instances of classes.
static ( static) can be:
- variables (also known as class variables)
- methods (also known as class methods)
- code block
- nested class
1. Java static variables
If a variable is declared as static, it is called a static variable.
- Static variables can be used to refer to properties common to all objects (not unique to each object). Such as: employee company name, student's university name.
Advantages of static variables:
- It makes program memory efficient (ie it saves memory).
Understanding the problem of not using static variables
class Student{
int rollno;
String name;
String college="ITS";
}
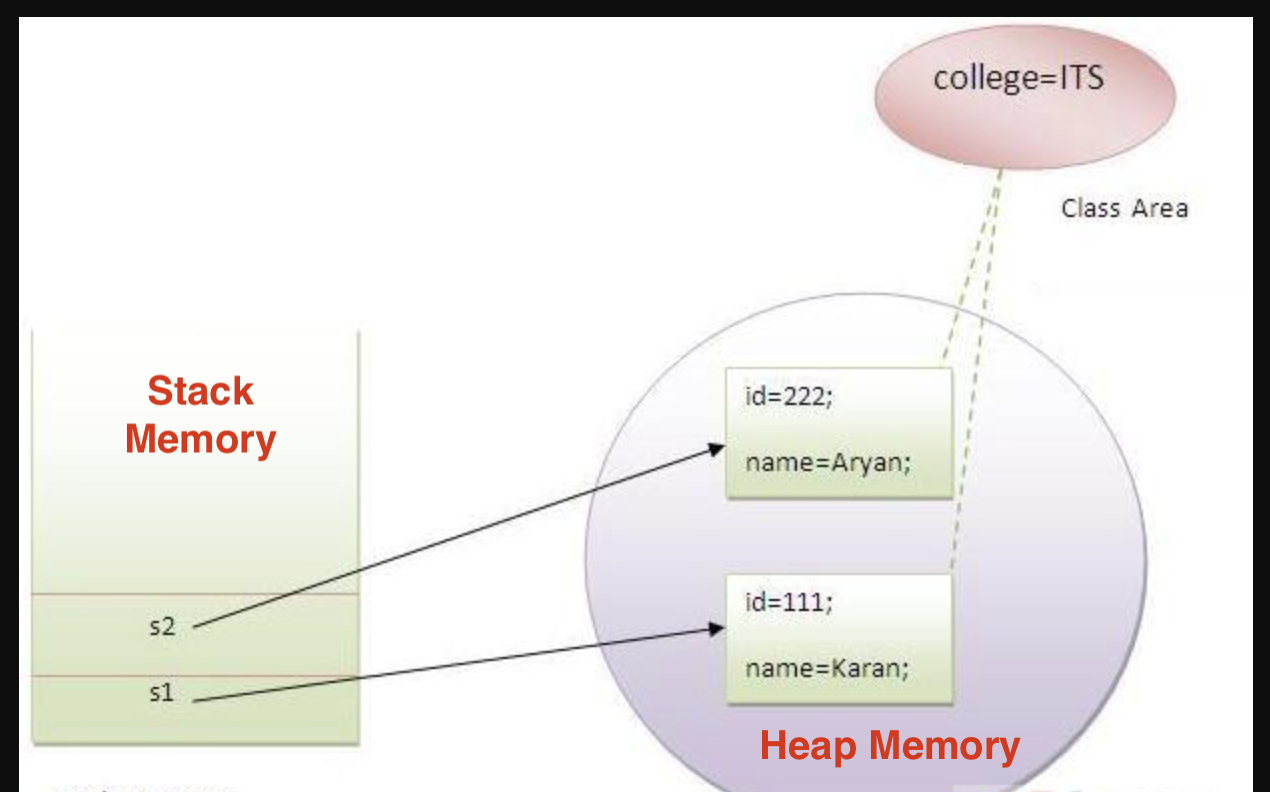
500 Say there are students in a school , now all instance data members will get memory every time the object is created. All students have their unique enrollment id: rollno and name so there is nothing wrong with instance data members. college Refers to the common properties of all objects. If you make it static (using the static keyword modify), this field will only get memory once.
Java static properties are shared to all objects.
Examples of static variables
//Program of static variable
class Student8 {
int rollno;
String name;
static String college = "ITS";
Student8(int r, String n) {
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + college);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student8 s1 = new Student8(111, "Karan");
Student8 s2 = new Student8(222, "Aryan");
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
The result of the above code execution is as follows −
111 Karan ITS
222 Aryan ITS
An example diagram of creating an object is shown below −
 |
Counter program without using static variables
In this example, we create an count instance variable called statistic to count the number of objects created, which is incremented in the constructor. Since instance variables take memory when the object is created, each object will have a copy of the instance variable, and if it is incremented, it will not be reflected in other objects. So the value of each object in the countvariable is still 1.
class Counter {
int count = 0;// will get memory when instance is created
Counter() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Counter c1 = new Counter();
Counter c2 = new Counter();
Counter c3 = new Counter();
}
}
The result of the above code execution is as follows −
1
1
1
The procedure for counter static variable is
as above, the static variable will get the memory only once, if any object changes the value of the static variable, it will keep its value, all instances can access the same variable value.
class Counter2 {
static int count = 0;// will get memory only once and retain its value
Counter2() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Counter2 c1 = new Counter2();
Counter2 c2 = new Counter2();
Counter2 c3 = new Counter2();
}
}
The result of the above code execution is as follows −
1
2
3
2. Java static method
If the keyword is applied on any method static, this method is called a static method.
- Static methods belong to the class, not to objects of the class.
- Static methods can be called directly without creating an instance of the class.
- Static methods can access static data members and can change the value of static data members.
Java Static Method Example
//Program of changing the common property of all objects(static field).
class Student9 {
int rollno;
String name;
static String college = "ITS";
static void change() {
college = "BBDIT";
}
Student9(int r, String n) {
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + college);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student9.change();
Student9 s1 = new Student9(111, "Karan");
Student9 s2 = new Student9(222, "Aryan");
Student9 s3 = new Student9(333, "Sonoo");
s1.display();
s2.display();
s3.display();
}
}
111 Karan BBDIT
222 Aryan BBDIT
333 Sonoo BBDIT
//Program to get cube of a given number by static method
class Calculate {
static int cube(int x) {
return x * x * x;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result = Calculate.cube(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
125
Static Method Limitations
Static methods have two major limitations. they are, respectively:
- Static methods cannot directly use non-static data members or call non-static methods.
thisThe andsupertwo keywords cannot be used in static context
class A {
int a = 40;// non static
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
The above code return
Compile Time Error
class A2 {
static {
System.out.println("static block is invoked");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello main");
}
}
static block is invoked
Hello main
class A3 {
static {
System.out.println("static block is invoked");
System.exit(0);
}
}
static block is invoked