Python Scale - Tkinter Scale Range widget
Scale widget whenever you need to choose a precise value from a range of values. It includes a sliding bar that allows picking values by dragging clockwise or from up to down, based on how your sliding bar is oriented
You use the Scale widget whenever you need to choose a precise value from a range of values. It includes a sliding bar that allows picking values by dragging clockwise or from up to down, based on how your sliding bar is oriented.
In this tutorial, we'll go through making a Tkinter scale.
Syntax
|
S= scale (root, option1, option2, option3…) |
Tkinter Scales Options
Here are some of the most typical options for creating a Tkinter scale:
-
Bg- defines the color of the background.
-
Fg- determines the color of the foreground.
-
Bd- specifies the scale widget's border.
-
Orient- either vertically or horizontally orients the scale.
-
From-The scale's starting value.
-
To-defines the scale's final value
-
Troughcolor- determines the color of the trough.
-
State- determines whether it is active or inactive.
-
Label- shows the scale's chosen value.
-
Pointer- defines how the cursor behaves when it hovers over a widget.
-
Highlighbackground- defines the color focus.
The Methods used to create the Tkinter scale.
Here are the two most typical approaches for building a Tkinter scale widget:
-
get() retrieves the scale value
-
get() retrieves the scale value
Examples of the Tkinter Scale
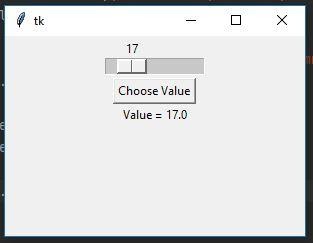
Example 1: A horizontal Tkinter scale
|
from tkinter import * def select():sel = "Value = " + str(v.get()) label.config(text=sel) top = Tk() top.geometry("300x200") v = DoubleVar() scale = Scale(top, variable=v, from_=1, to=100, orient=HORIZONTAL) scale.pack(anchor=CENTER) btn = Button(top, text="Choose Value", command=select) btn.pack(anchor=CENTER) label = Label(top) label.pack() top.mainloop()
|
 |
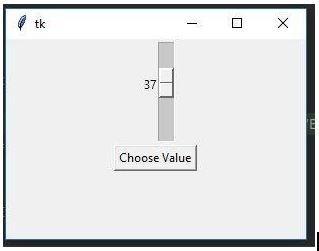
Example 2: A vertical Tkinter scale
|
from tkinter import * def select():sel = "Value = " + str(v.get()) label.config(text=sel) top = Tk() top.geometry("300x200") v = DoubleVar() scale = Scale(top, variable=v, from_=1, to=100, orient=VERTICAL) scale.pack(anchor=CENTER) btn = Button(top, text="Choose Value", command=select) btn.pack(anchor=CENTER) label = Label(top) label.pack() top.mainloop()
|
 |