Position Tkinter topLevel Widget in Python with RRutors
Learn to build popup modal windows in Tkinter with top-level widgets, including buttons, text, and frames for a more interactive user interface at rrtutors.com
Tkinter's top-level widget is used to build a popup modal window. The popup window created by the top-level window has the same appearance as the default in the tkinter program. If you want to incorporate widgets, you may do so by including text widgets, button widgets, a frame, and other components.
Having the top-level window resizable enables you to change its size and location on the screen. Widgets are always on top of other windows when you open a new one on the top level.
Winfo x() and Winfo y() are two ways to get the root window's position in the system (). The top-level widget may then be repositioned in relation to the root window using the geometry approach. Because the top-level widgets are positioned relative to the root window, they are distinct from one another. Let's have a look at the following code snippet
|
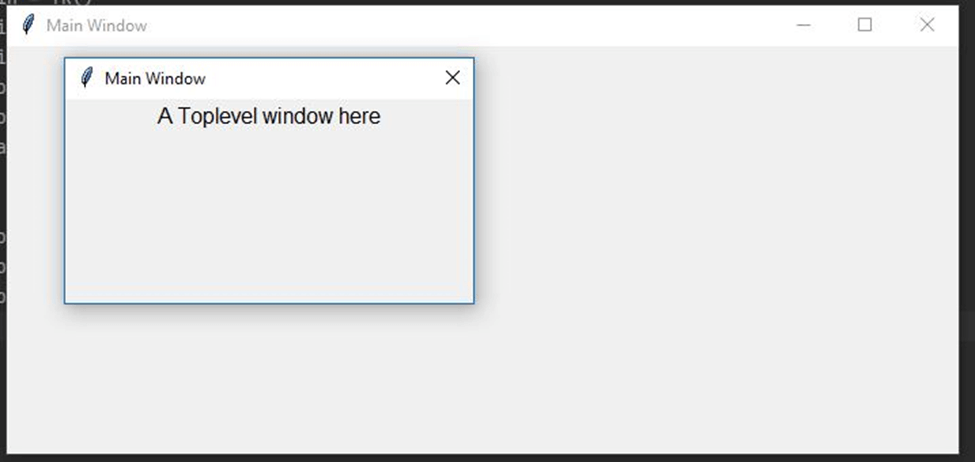
from tkinter import * win = Tk() win.geometry("700x300") win.title("Main Window") top = Toplevel(win) top.geometry("300x150") Label(top, text= "A Toplevel window here", font="Calibri, 12").pack() x = win.winfo_x() y = win.winfo_y() top.geometry("+%d+%d" %(x+200,y+200)) top.wm_transient(win) top.mainloop()
|
Output
When you execute this code, two windows will appear on your screen: a parent window and a top level window
 |