Django Tutorial - MVT Pattern on Django (Model View Template)
Django tutorial series we will cover design pattern in Django. This design pattern is MVT design pattern. Let's discuss about MVT The MVT (Model View Template) is a software design pattern. This MVT design pattern consist of three important components which are named as Model, View and Template. Similarly Django follows the MVC pattern but it maintains its own conventions
In this Django tutorial series we will cover design pattern in Django. This design pattern is MVT design pattern. Let's discuss about MVT
The MVT (Model View Template) is a software design pattern. This MVT design pattern consist of three important components which are named as Model, View and Template. Similarly Django follows the MVC pattern but it maintains its own conventions. So, control is handled by the Django framework itself
Model
Basically Model act as Meditator Between the Website Interface and the Database. In Django, We use Python Classes To make Models Which is nothing but a Table in a Database. Class Attributes is Columns of the Table in the database and on these attributes we can set constraints like primary key, foreign key, Many to Many Relation, one to many Relation, etc. So using Models in Django makes it easy to connect with the database. or we can say that model is the whole logic of your project or business
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=200)
email = models.EmailField()
|
View
The View is used to execute the business logic and interact with a model to carry data and renders a template. The view can be a function-based view or can be Class-based view. when the user requests something there is basically a function or class is written to handle those requests. for example when the user request ‘www.yoursitename.com/home’. so basically here user requested for the home page of your site and after this, the view you have written to handle this particular request will return the response to the user in the form of an HTML file or we can say that HTTP response
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import Author
# create a function (view)
def author_view(request):
template_name="author.html"
author=Author.objects.get(id=1)
return render(request, template_name, {"author":author})
|
Template
In Django, Templates are nothing but the HTML file which handles the User Interface part completely. These Templates rendered when the user requests these templates. So basically templates are returned response by the view to the user requests
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Author Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to {{ author.name }} Page</h1>
<p> Email Id : {{ author.email }}</p>
</body>
</html>
|
So let's look at this in Picture
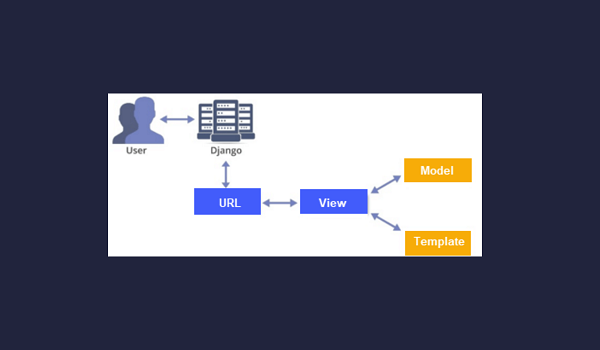 |
Here you can see that user requests to your Django site. user has written some URL (Uniform Resource Locator) like www.yoursite_name.com/page_name after this, URL will match to the specified View, Now View will check the request object if there are any attributes related to Database it will fetch from or save those attributes to the database. If there are no Attributes related to the Database simply it will look for an HTML page (templates) to return a response but if it doesn’t found any templates it will show the error “404 pages nor found”
#Django, #Design pattern, #MVT Design Pattern