Jetpack ViewModel Tutorial for Android with RRutors
Learn about ViewModel, an Architecture component that survives configuration changes and preserves data. Master ViewModel on rrtutors.com. Start coding today!
In this post we are going to cover Jetpack android component ViewModel.
- What is ViewModel
- Why do we need ViewModel
When we start android application one of the most common thing is handle configuration changes of the application.
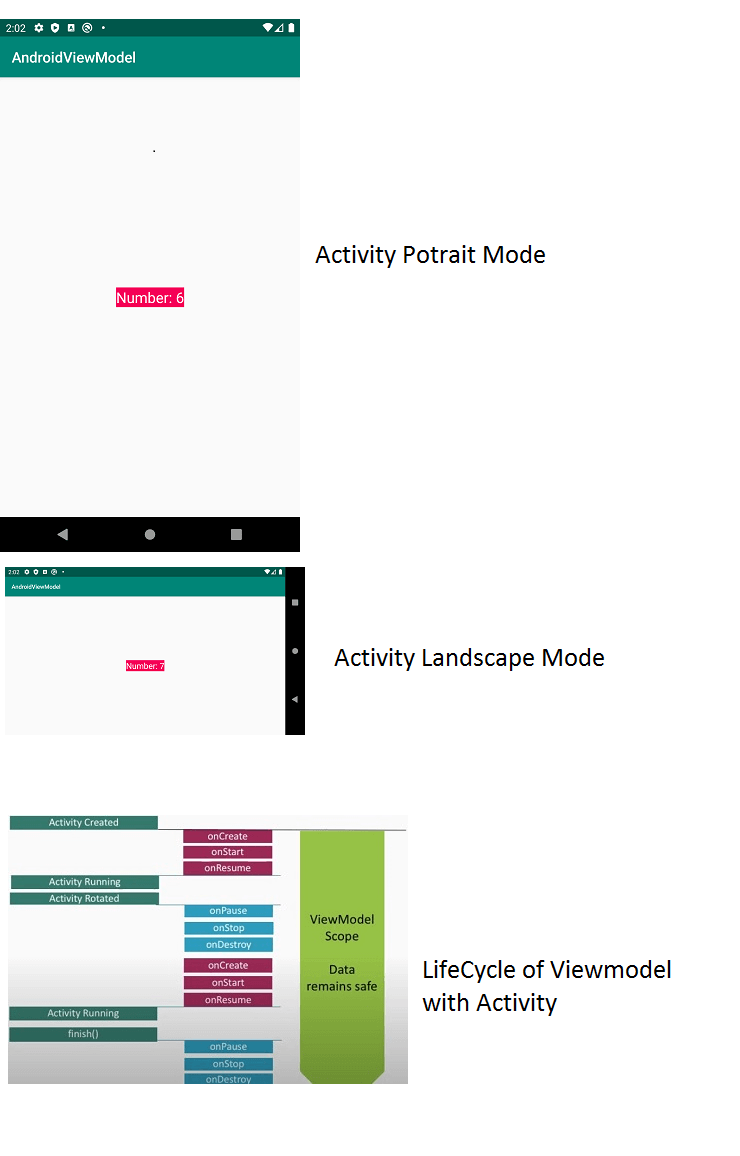
Suppose i have an activity which showa the random number generation and display it.
Lets configuration changes will be occur like screen rotation.
Now Lets rotate device, on rotation of the device the activity destroy and activity reloaded and the random number generated again, means the old data lost and new data generated.
So we won't user to lost data on configuration changes. To do this we will use ViewModel
What is ViewModel?
ViewModel is a class which provides the data to UI like Activities and Fragments.
Now when activity in portrait mode it will fetch data from ViewModel and when device rotated the ViewModel pass the same data to recreated activity in Landscape Mode
LifeCycle of ViewModel
When i start application my activity in portrait mode. When activity created we are linking our ViewModel to activity. This ViewModel will be alive until unless created activity completely destroyed.
When activity created in portrait mode the Lifecycle methods of onCreate,onStart,onResume will executed and activity is in running state.
Now rotate the device the activity will rotate from portrait mode to Landscape Mode. Now onPause,onStop and onDestroy methods will executes.
When activity in Landscape mode again onCreate,onStart,onResume will executed and activity is in running state in Landscape mode.
Thus the data created in portrait mode will store in ViewModel and restore it in Landscape mode.
Now if i close application, our activity will be completely destroyed and onPause,onStop and onDestroy methods will executed and our ViewModel also get cleared. So when activity get completely destroyed it associated ViewModel onCleared() method will executes and destroy completely.
In this onCleared() we can perform cleaning of resources and free up memory
The ViewModel will be act like a bridge between Views and data repositories. ViewModel contains all business logic for the application
Lets check Example
Step 1: Create Android Application
Step 2: Add dependencies for ViewModel class
Step 3: Create a Class which will generate Random number
Without ViewModel
MainActivity.java
|
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { TextView txt_mynumber; } |
DataRepository.java
|
public class DataRepository { |
Output
|
Now if we run the application Log will prints on Rotating device Means every time new Random number will generated |
With ViewModel
MainActivity.java
|
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { TextView txt_mynumber; } |
In the above example code to access views inside the class by using findViewById() property. With findviewById() length of the class file be increased. To over come this and access views directlly by using the View Binding Technique
DataRepository.java
|
package com.rrtutors.androidviewmodel; import android.util.Log; import java.util.Random; import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel; public class DataRepository extends ViewModel { @Override |
Output
|
Myrandom Created Number on Ratating device means on ration ViewModel will persist the data and restore it |